Molybdenum
| Isotope | Atomic mass (Da) | Isotopic abundance (amount fraction) |
|---|---|---|
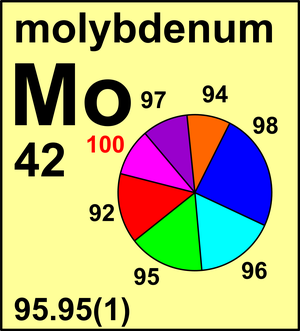
| 92Mo | 91.906 807(1) | 0.146 49(106) |
| 94Mo | 93.905 084(1) | 0.091 87(33) |
| 95Mo | 94.905 8374(8) | 0.158 73(30) |
| 96Mo | 95.904 6748(8) | 0.166 73(8) |
| 97Mo | 96.906 017(1) | 0.095 82(15) |
| 98Mo | 97.905 404(1) | 0.242 92(80) |
| 100Mo | 99.907 468(2) | 0.097 44(65) |
In its 1961 report, the Commission recommended Ar(Mo) = 95.94 based on the chemical ratio measurements. Recalculation of their measurements based on current values of Ar(Ag) and Ar(Cl) gives Ar(Mo) = 95.939. In its 1975 report, the Commission evaluated five manuscripts dealing with mass-spectrometric determinations of the isotopic composition of molybdenum. Although they were judged not to be of equal reliability, their results all fall in the range of Ar = 95.93 to 95.94 in close agreement with the chemical value. Standard atomic weight of molybdenum was changed to its current value in 2013 as a result of a re-evaluation of isotopic measurements. The annotation "g" refers to anomalous occurrences at the Oklo natural nuclear reactor in Gabon.
© IUPAC 2003
CIAAW
Molybdenum
Ar(Mo) = 95.95(1) since 2013
The name derives from the Greek molybdos for "lead". The ancients used the term "lead" for any black
mineral that leaves a mark on paper. Molybdenum was discovered by the Swedish pharmacist and
chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele in 1778. It was first isolated by the Swedish chemist Peter-Jacob Hjelm
in 1781.
Isotopic reference materials of molybdenum.